NEWSNEWS
Featured products
Contact Us
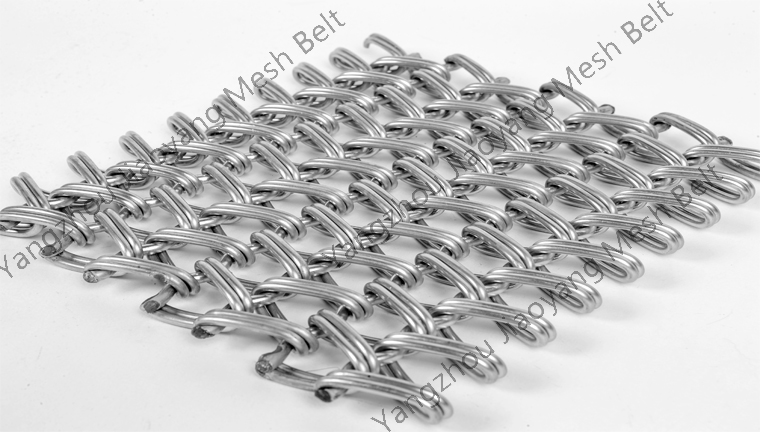
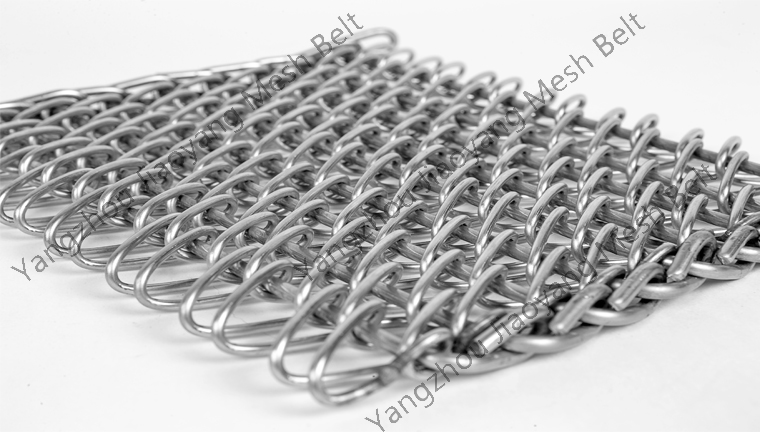
Mesh Belt Selection and Use: Reasons for Severe Deformation of Mesh Belts in Sintering Furnaces
2025-12-15Many people in industries such as powder metallurgy, electronic components, ceramic products, and solar photovoltaics have encountered the following problem: severe deformation of the mesh belt in sintering furnaces. What are the causes? Based on years of practical experience, Jiaoyang has summarized several common phenomena.
Specifications and Dimensions
A mismatch between the conveyor belt width and the furnace dimensions can cause deformation; too wide a belt will cause edge friction, while too narrow a belt will result in uneven stress distribution.
Inaccurate calculation of the conveyor belt length will lead to uneven tension distribution during operation.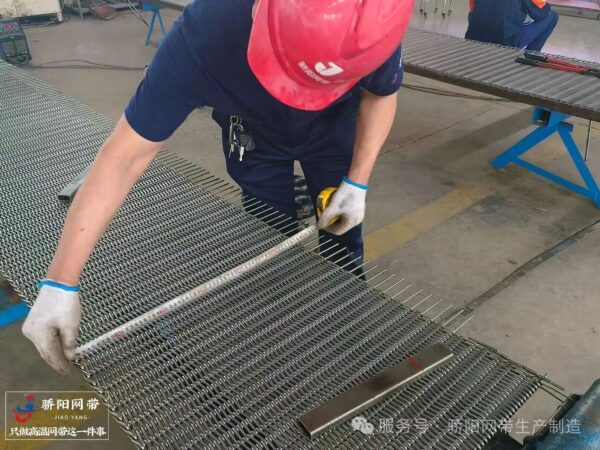
Overheating and Overload
Uneven heating or overall overheating of the sintering furnace mesh belt can lead to localized or overall elongation, misalignment, etc.
Overloading or uneven material placement can cause the mesh belt to gradually deviate from its track during operation, resulting in friction and compression between the edges and the furnace body, which can lead to deformation over time.
Improper Use
Incorrect orientation when a new mesh belt is introduced into the furnace can cause unevenness on the mesh surface, making it difficult to transport materials smoothly.
Material getting stuck between the mesh belt and rollers or baffles, without timely cleaning and stopping, can cause the mesh belt to be torn, scratched, or forcibly broken.
Excessive or insufficient tension in the sintering furnace mesh belt can cause deformation and increase energy consumption.
Frequent start-ups and shutdowns of the sintering furnace, or excessively rapid heating/cooling rates, can generate enormous thermal stress, causing cracks in the mesh belt.