NEWSNEWS
Featured products
Contact Us
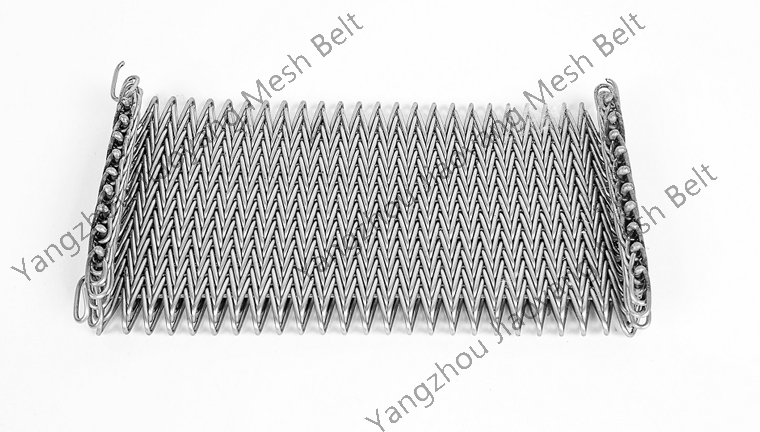
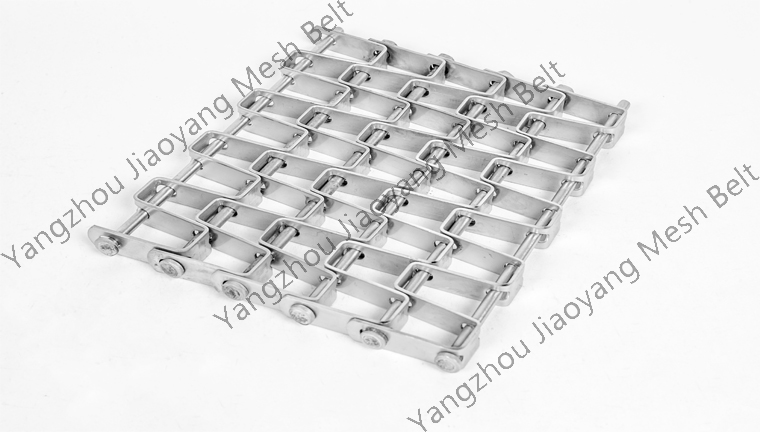
analysis of the types of equipment that will use stainless steel conveyor mesh belts:
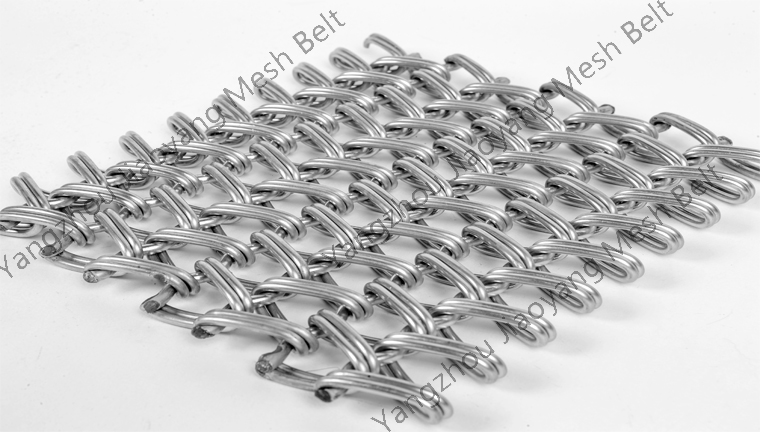
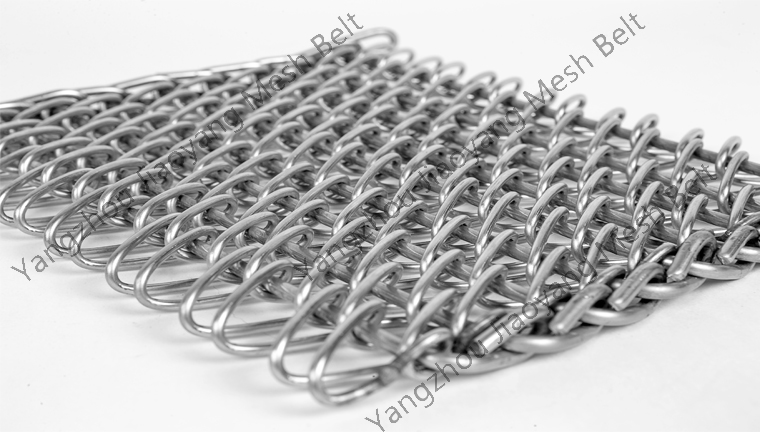
2024-03-29Stainless steel conveyor mesh belt product characteristics (high temperature resistance, corrosion resistance, load-bearing, continuous conveying), combined with the understanding of the working principle of the quenching furnace, the following is an analysis of the types of equipment that will use stainless steel conveyor mesh belts:
Core screening criteria:
Continuous production: materials need to move continuously in the furnace.
Mesh belt structure: clearly use mesh belt as a conveying carrier.
High temperature, corrosive environment: the advantageous application scenario of stainless steel mesh belt.
Clearly use the type of quenching furnace where stainless steel conveyor mesh belts will be used
Continuous Quenching Furnace (Continuous Quenching Furnace)
Reason: This is the most typical application scenario. The core of the continuous furnace is to continuously deliver the workpiece into the heating zone, insulation zone, quenching tank and tempering zone (if any) through a conveying system (such as mesh belt, roller, chain). Stainless steel mesh belts are very suitable for this scenario that needs to withstand high temperatures, carry workpieces and run continuously.
Stainless Steel Bright Quenching Furnace & High Quality Stainless Steel Bright Quenching Furnace
Reason: The name of the furnace directly points out that stainless steel is used, and bright quenching usually requires a protective atmosphere (such as ammonia decomposition gas, hydrogen) or vacuum. Stainless steel mesh belts are resistant to high temperatures and are not easy to react with the atmosphere to contaminate the workpiece, making them an ideal choice for this type of furnace. The mesh belt is a core component as a support and conveying component for the workpiece.
Aluminium Drop Quench Furnaces / Aluminum Quenching Furnace / Aluminum Alloy Quenching Furnace
Reason: Continuous mesh belt furnaces are widely used for heat treatment of aluminum alloys (especially T6 solution treatment). The workpiece is evenly heated and insulated on the mesh belt through the heating zone, and then quickly transferred to the quenching medium (usually water). The mesh belt needs to withstand the heating temperature of the aluminum alloy (~500°C) and be resistant to water vapor corrosion. Stainless steel mesh belts are the mainstream choice.
Glass Melting Quenching Furnace (Glass Melting Quenching Furnace)
Reason: Continuous mesh belt furnaces are often used for heat treatment (such as tempering, annealing) of glass products (such as glassware and glass bottles). The mesh belt needs to withstand the high temperature of the glass and has a smooth surface that is not easy to damage the glass. Stainless steel mesh belts are widely used.
Quenching Furnace (Quenching Furnace) / Quenching Furnaces (Quenching Furnaces – plural)
Reason: This is a very broad term, but a large part of it refers to continuous mesh belt quenching furnaces. When customers search for this general term, your mesh belt product is a relevant solution.
Heat Treatment Furnace with Quenching (Heat Treatment Furnace with Quenching Function)
Reason: It is also a broad term, but it includes all heat treatment furnaces with integrated quenching function. Among them, furnace types with continuous belt conveyor systems (such as mesh belt furnaces) are an important part.
Quenching furnace types that may use stainless steel conveyor belts (depending on the specific design)
Batch Integral Quench Furnace
Possibility: Traditional box-type integral quenching furnaces usually use trays or baskets, without conveyor belts. However, if it is designed as a push rod, rotary bottom or conveyor belt type “continuous” or “semi-continuous” batch processing furnace, it is possible to use a mesh belt or similar conveying mechanism. The equipment structure needs to be analyzed specifically.
Salt Quenching Furnace
Possibility: Salt bath furnaces themselves usually do not use mesh belts. However, in salt bath quenching production lines, workpieces may need to be transported in and out of the salt bath tank or connected to the previous and subsequent processes (such as cleaning, preheating, tempering) by stainless steel mesh belts. The mesh belt needs to be extremely resistant to molten salt corrosion, and special stainless steel (such as 310S, 314) mesh belts are possible options.
Surface Quench Furnace
Possibility: If surface hardening (e.g. induction hardening) is integrated into a continuous production line (e.g. pretreatment -> heating -> surface hardening -> tempering), then the conveyor mechanism connecting the heating and hardening stations may use a mesh belt. Pure induction hardening equipment by itself usually does not use a mesh belt.
Specify the types of quenching furnaces where a conveyor belt is unlikely or unsuitable
Sealed Quench Furnace (Sealed Quench Furnace) and all variants (Integral Quench, Ipsen, Unitherm, etc.): This type of furnace is a typical chamber furnace/pit furnace. The workpiece (usually in a basket) is heated, carburized (if necessary) and quenched (oil or gas) in the same sealed chamber. There is no need for continuous conveying, and a conveyor belt is not used. Baskets or trays are used.
Drop Bottom Quench Furnace / Drop Quench Furnace (Bottom Open/Drop Quench Furnace): The workpiece is heated in a basket above the furnace, then the entire basket or furnace bottom is opened and the workpiece drops directly into the quenching tank below. There is no conveyor belt.
Car Bottom Quenching Furnace (Car Bottom Quenching Furnace): The workpiece is loaded on a car, which is pushed into the furnace for heating, and then pulled out with the car for quenching (or the car itself has a quenching tank). A car is used, and no conveyor belt is used.
Vacuum Furnace (Vacuum Furnace) and all variants (Gas Quench, Oil Quench, Vacuum Quenching, etc.): Vacuum furnaces (whether single chamber, double chamber, gas quenching, oil quenching) are highly sealed inside a vacuum or high-pressure inert gas environment. The workpiece is usually placed on a fixed rack, basket or tray. There is no continuous conveyor belt mechanism in the furnace and it is not suitable for installation. External conveying mechanisms may be required for entering and exiting the furnace, but mesh belts are not used in the core heating/quenching zone of the furnace.
Internal/External Quench Vacuum Furnace (Internal/External Quench Vacuum Furnace): As mentioned above, mesh belts are not used in vacuum furnaces.
High Pressure Gas Quenching Furnace (High Pressure Gas Quenching Furnace): Usually refers to vacuum high pressure gas quenching furnaces or specially designed atmospheric high pressure gas quenching box furnaces. Mesh belts are not used.
Oil Quenching Furnace (Oil Quenching Furnace): This term usually refers to the quench tank itself or an integral quenching furnace (such as box type, pit type) with an integrated heating chamber. It does not refer to a continuous conveyor mesh belt furnace.
Water Quench Furnace (Water Quench Furnace): Mainly refers to the quench tank. If it refers to equipment, it is usually a box type, pit type or conveyor chain (plate) type furnace. Mesh belts are not often used in situations where they are directly exposed to strong water flow impact. Chain or plate conveyors are more common.
Furnace Quenching Oil / Furnace Water Quencher (Furnace Quenching Oil / Furnace Water Quencher): refers to the medium, not the furnace type.
Quench Furnace Brick Interior / Quench Furnace Interior / Surface Quench Furnace Interior Bricks (Quench Furnace Lining Bricks): refers to the furnace structure material.
Quench Furnace Manufacturers / Suppliers / Meaning (Quench Furnace Manufacturers / Suppliers / Meaning): refers to the equipment supplier or definition.
Quench Furnace Filtration (Quench Furnace Filtration): refers to the filtration system of the quenching medium.
Vertical Tube Quench Test Furnace (Vertical Tube Quench Test Furnace): Usually a small experimental device, the workpiece is suspended or placed, and no conveyor belt is used.
Structural keywords (such as Carburization quench furnace brick interior, furnace aerated water quencher, quenching furnace mechanism, sealed quench furnace design/details/operation/safety/pdf/ppt/process/wiki/wikipedia/working/working principle): These describe the structure, principle, operation or documentation of the furnace, not whether the furnace type itself uses mesh belt.
Abstract/non-equipment keywords (such as faith quenches the furnace of fire, quench a furnace, quench furnace meaning): non-physical equipment terms.
Specific material processing furnace (such as Titanium, Molten Salt for knives, High Speed Steel): Titanium alloy, high-speed steel quenching multi-purpose vacuum furnace or special atmosphere protection furnace (box type, pit type), molten salt bath furnace itself does not use mesh belt (but front and rear conveying may be used). Unless it is clearly a continuous mesh belt furnace design.