Introduction
Stainless steel conveyor mesh belts are critical components in industrial heat treatment processes, particularly in quenching operations. Their unique combination of high-temperature resistance, corrosion resistance, load-bearing capacity, and continuous conveying capability makes them ideal for specific types of quenching furnaces.
This technical analysis examines various quenching furnace types to identify where stainless steel mesh belts are essential components, where they may be applicable depending on design, and where they are unsuitable based on furnace structure and operating principles.
Core Selection Criteria
Fundamental requirements for mesh belt utilization
Continuous Production
Materials need to move continuously through the furnace chamber, requiring a conveying mechanism.
Mesh Belt Structure
Equipment explicitly designed to use mesh belts as the primary conveying medium.
High-Temperature Environment
Operating temperatures typically exceeding 400°C where stainless steel properties are essential.
Furnace Type Analysis
Core Applications
Mesh belts are essential components
- Continuous Quenching Furnace – Primary conveying mechanism
- Stainless Steel Bright Quenching Furnace – Required for surface quality
- Aluminum Quenching Furnace – Standard for T6 solution treatment
- Glass Melting Quenching Furnace – Smooth surface handling
- General Quenching Furnaces – When designed as continuous systems
Technical Rationale: These furnace types fundamentally rely on continuous mesh belt systems for material handling through heating, quenching, and cooling zones. Stainless steel construction withstands process temperatures (typically 400-1100°C) while resisting corrosion from quenching media vapors.
Possible Applications
Dependent on specific design
- Batch Integral Quench Furnace – Only in continuous variants
- Salt Quenching Furnace – For production line connections
- Surface Quench Furnace – In integrated production lines
Technical Rationale: Mesh belts may be used in auxiliary roles or in specially designed continuous versions of typically batch-based systems. Material compatibility must be carefully evaluated (e.g., specialized stainless alloys like 310S/314 for salt environments).
Unsuitable Applications
Incompatible with mesh belt systems
- Sealed Quench Furnaces – Batch processing design
- Vacuum Quenching Furnaces – Require sealed environments
- Drop Bottom Quench Furnaces – Gravity-based transfer
- High Pressure Gas Quench – Pressure vessel constraints
- Car Bottom Quenching – Uses rail-based transfer
Technical Rationale: These furnace types employ alternative material handling methods such as static baskets, carts, or gravity-based transfer that eliminate the need for continuous conveying systems. Structural and operational constraints also prevent mesh belt integration.
Application Comparison
| Furnace Type | Application Suitability | Temperature Range | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Continuous Quenching Furnace | Essential | 500-1100°C | Primary conveying mechanism |
| Aluminum Quenching Furnace | Essential | 450-550°C | Rapid transfer to quench tank required |
| Stainless Steel Bright Quenching | Essential | 800-1050°C | Surface quality preservation |
| Salt Quenching Production Line | Possible (Auxiliary) | 200-600°C | Requires specialized corrosion-resistant alloys |
| Surface Quench Integrated Line | Possible (Connecting) | Varies | Material handling between stations |
| Sealed Quench Furnace | Unsuitable | 850-950°C | Batch processing with baskets |
| Vacuum Quenching Furnace | Unsuitable | 1000-1300°C | Sealed environment constraints |
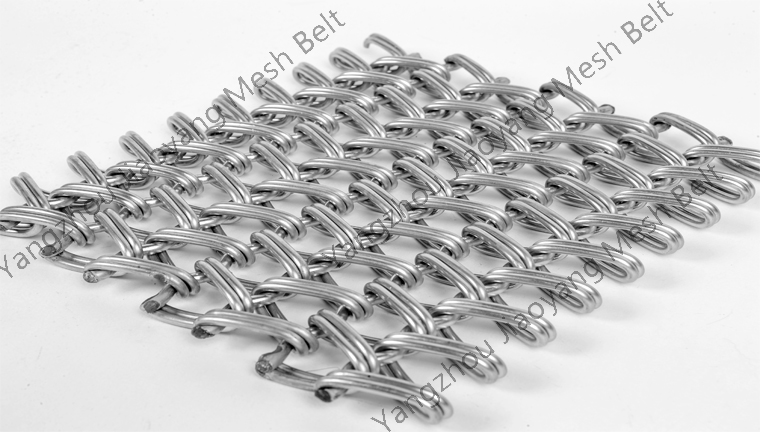
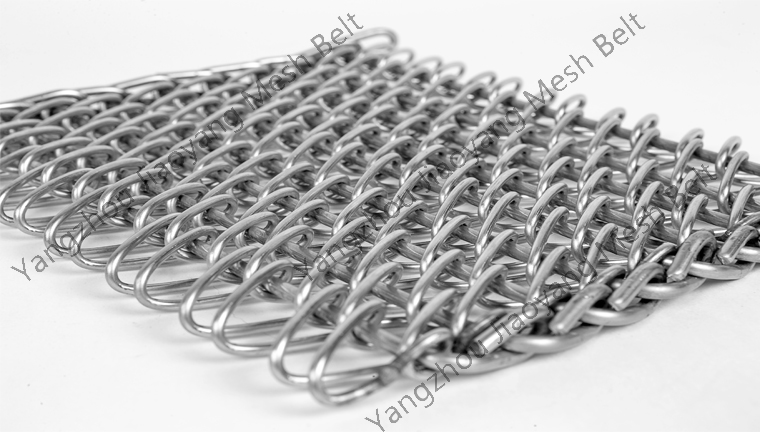
Key Mesh Belt Properties
High-Temperature Resistance
Withstands continuous operation at 1100°C+ with minimal deformation or degradation
Corrosion Resistance
Excellent resistance to quenching media vapors, salt atmospheres, and process chemicals
Load-Bearing Capacity
Robust construction supports heavy industrial loads with minimal stretching
Continuous Operation
Designed for 24/7 operation with minimal maintenance requirements
Technical Recommendations
Based on this analysis, manufacturers should prioritize mesh belt solutions for continuous quenching applications where high-temperature stability and corrosion resistance are critical performance factors.
Focus Areas
Prioritize continuous quenching systems for aluminum, stainless steel bright quenching, and glass treatment applications
Key Properties
Emphasize high-temperature stability (1100°C+), corrosion resistance, and load capacity in technical specifications
Market Strategy
Target manufacturers of continuous quenching systems with tailored solutions for specific industry applications