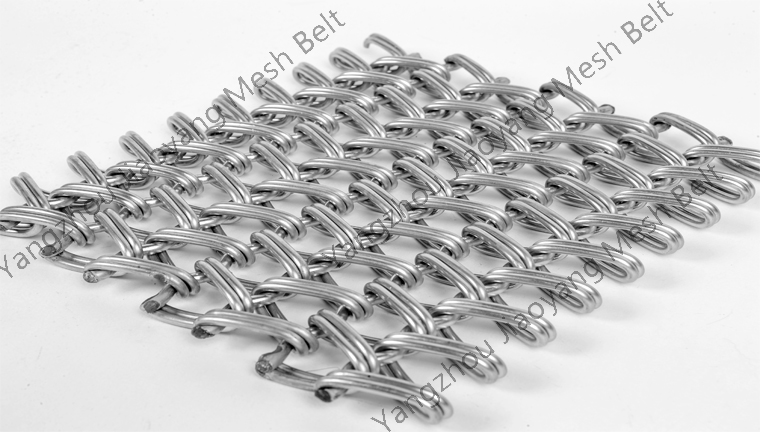
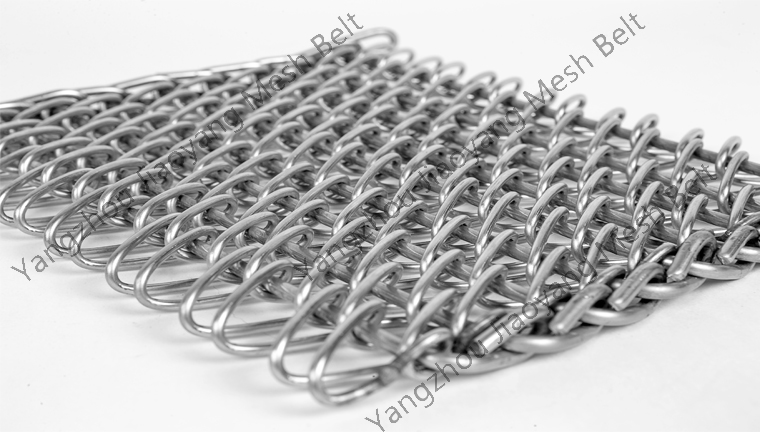
NEWSNEWS
Featured products
Contact Us
Nitriding Surface Treatment: Process & Technical Specifications
2025-06-25Nitriding Surface Treatment: Process & Technical Specifications
Nitriding is a thermochemical surface treatment process where nitrogen atoms diffuse into a workpiece’s surface layer under controlled temperature and medium conditions. Primary methods include liquid nitriding, gas nitriding, and plasma (ion) nitriding.
Core Process Fundamentals
-
Gas Nitriding Mechanism
Workpieces are sealed in a retort with flowing ammonia gas (NH₃). At 500-590°C, ammonia decomposes into active nitrogen atoms that adsorb onto and diffuse into the surface, modifying its chemical composition and microstructure to enhance surface properties. -
Nitrocarburizing Variant
When carbon is simultaneously introduced to accelerate nitrogen diffusion, the process becomes nitrocarburizing (also known as ferritic nitrocarburizing).
Pre-Treatment Requirements
1. Heat Treatment Conditioning
-
Quenching & Tempering:
Must achieve tempered sorbite microstructure.
Critical Parameter: Tempering temperature > Subsequent nitriding temperature.
2. Stress Relief Protocol
-
Annealing temperature < Prior tempering temperature
-
Extended dwell time (exceeding standard tempering duration)
-
Controlled slow cooling to room temperature
-
Note:
-
Avoid normalizing for large cross-sections
-
Tool steels require quenching/tempering (annealing prohibited)
-
Workpiece Preparation Standards
| Requirement | Specification |
|---|---|
| Surface Roughness (Ra) | < 1.6 μm |
| Surface Defects | Zero scratches/dents/corrosion |
| Interim Corrosion Protection | Coating with rust-preventive oil |
| Pre-Nitriding Cleaning | Wipe with solvent (e.g., clean gasoline) |
Geometric Limitations
-
✘ Sharp edges/corners (risk of embrittlement)
-
✘ Unmachined surfaces (grinding mandatory)
-
✘ Partial-coverage methods using machining allowances
Process Comparison Table
| Method | Temperature Range | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gas Nitriding | 500-590°C | Deep case depth (>0.5mm) | Long cycle time (20-100h) |
| Plasma Nitriding | 350-600°C | Precise control, reduced distortion | Equipment complexity |
| Liquid Nitriding | 510-580°C | Rapid processing (1-4h) | Cyanide salt baths |
Technical Footnotes
-
Salt bath nitriding typically uses cyanide-containing compounds (e.g., NaCN) – require eco-friendly disposal
-
Post-nitriding surface porosity may necessitate honing/polishing for precision components
-
Case depth follows Fick’s diffusion law: Depth ∝ √(Time × Temperature)
Compliance Note: AMS 2759/10, ASTM E18, and ISO 9001:2015 standards govern critical aerospace/automotive applications.