NEWSNEWS
Featured products
Contact Us
How to Quench Through a Conveyor Furnace
2025-07-11Understanding the Conveyor Furnace
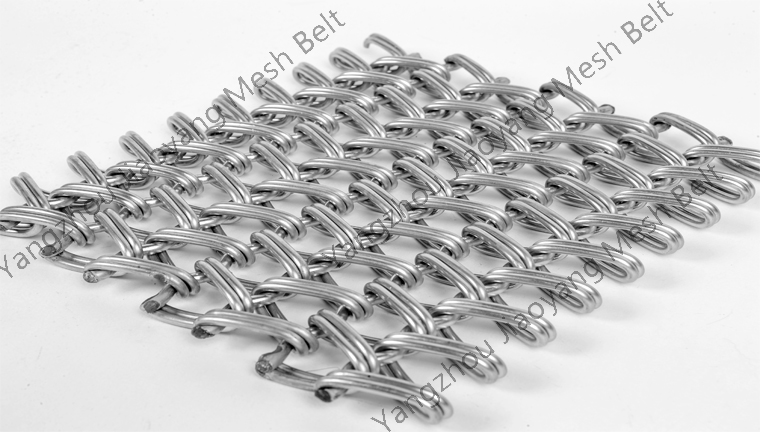
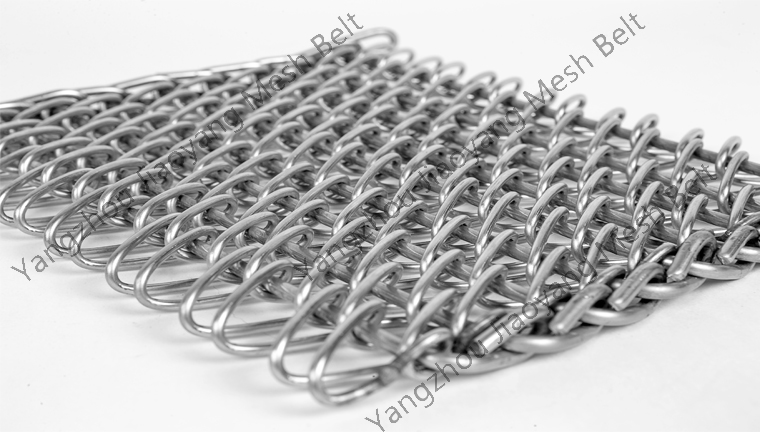
A conveyor furnace is a type of furnace that consists of a steel frame and a refractory lining, typically made of silicon carbide fiber or lightweight firebrick. It is equipped with heating elements at the top and bottom, and a conveyor belt inside the furnace chamber. The conveyor belt transports workpieces through a temperature-controlled heating zone, achieving the desired heat treatment process. The furnace is composed of an inlet section, preheating section, sintering section, slow cooling section, water cooling section, and outlet section, with the conveyor belt transmission consisting of high-temperature resistant conveyor belts, transmission devices, etc.
Preparation before Quenching
Workpiece Preparation
- Clean the workpiece: Ensure that the surface of the workpiece is free from oil, rust, impurities, etc., to avoid affecting the quenching effect. For example, screws and other workpieces should be cleaned before being placed in the conveyor furnace to ensure a clean surface.
- Check the size and shape of the workpiece: Confirm that the size and shape of the workpiece meet the processing requirements of the conveyor furnace, avoiding issues caused by oversized or unusually shaped workpieces during the quenching process.
Equipment Inspection and Adjustment
- Inspect the furnace body: Check for damage, cracks, etc., ensuring that the furnace body has good sealing properties. Inspect each part of the inlet section, preheating section, sintering section, slow cooling section, water cooling section, and outlet section to ensure they are functioning properly.
- Adjust the heating elements: Ensure that the heating elements can operate normally. Conduct a power test on them to check if the heating is uniform. Different heating elements have different performance characteristics, so it’s important to ensure they can heat the workpieces to the appropriate temperature.
- Inspect the conveyor belt transmission: Check for damage, deformation, etc., on the high-temperature resistant conveyor belt, and ensure that the transmission device operates smoothly, allowing the conveyor belt to transport the workpieces smoothly through each section.
- Adjust the temperature control system: Calibrate the temperature control system to ensure accurate control of heating temperature and time. During the heating process, the temperature should be slowly increased to avoid the generation of thermal stress, as workpieces expand when heated, and different parts may expand at different rates, leading to thermal stress.
Preparation of Quenching Medium
- Choose the appropriate quenching medium: Select the appropriate quenching medium based on the material of the workpiece. For example, medium carbon steel (such as 45 steel) usually uses water as the quenching medium, while alloy steel (such as 40Cr) uses oil or other specialized quenching fluids as the quenching medium.
- Check the quality of the quenching medium: If using quenching oil, check its quality and usage time. Poor oil quality or long usage time can lead to partial carbonization on the surface of the workpiece. Also, check if there are any impurities or water in the quenching medium, as impurities or water in the cooling medium may affect the quenching effect.
Quenching Process
Loading
Place the prepared workpieces evenly on the conveyor belt inside the conveyor furnace. Pay attention to proper stacking to avoid issues such as slight oxidation of the workpiece surface in the quenching oil due to improper stacking. The loading quantity should be reasonably controlled according to the processing capacity of the conveyor furnace.
Heating
- Set heating parameters: Set the appropriate heating temperature and holding time based on the material and quenching requirements of the workpiece. For example, for general steel, the steel needs to be heated above the critical temperature.
- Gradual heating: Start the conveyor furnace and allow the workpieces to slowly enter the heating area with the conveyor belt. Gradually increase the temperature within the set heating rate to avoid the generation of thermal stress. During the heating process, closely monitor the temperature changes inside the furnace to ensure that the temperature remains within the set range.
Quenching
- Enter the quenching area: When the workpieces reach the set temperature and hold for a certain period, they will enter the quenching area with the conveyor belt. If a dual-liquid reversing quenching device is used, guide the workpieces to the appropriate quenching medium according to their material. For example, different materials such as carbon steel and alloy steel are guided to the first quenching area or second quenching area respectively.
- Control the quenching process: Observe the cooling of the workpieces in the quenching medium, ensuring that they cool rapidly to achieve the purpose of quenching. Control the quenching time to avoid over- or under-quenching affecting the quenching effect.
Subsequent Processing
- Tempering: After quenching, the workpieces usually need to undergo tempering treatment to eliminate quenching stress and improve the toughness and stability of the workpieces. Place the quenched workpieces back into the conveyor furnace and heat and hold according to the tempering process requirements, then slowly cool.
- Cleaning and inspection: After tempering, remove the workpieces from the conveyor furnace and clean them to remove the quenching medium and impurities on the surface. Then conduct an appearance inspection and performance testing of the workpieces, such as checking hardness, strength, etc., to ensure they meet the requirements. If any issues are found, such as surface blackening or oxidation, analyze the cause and take appropriate measures to improve it.
Operation Precautions
- Comply with operating procedures: Operate strictly according to the operating procedures of the conveyor furnace, avoiding human violations of operating procedures or incorrect adjustments and modifications to the equipment, which may affect the entire quenching process and lead to a decline in the performance of the furnace or even accidents.
- Safety protection: Operators should wear protective equipment, such as high-temperature gloves and goggles, to prevent injury from high temperatures, flames, etc. during operation.
- Regular maintenance and care: Regularly maintain the conveyor furnace, clean up accumulated carbon and other impurities inside the furnace, and check the performance indicators of the equipment to ensure that the equipment is always in good working condition.