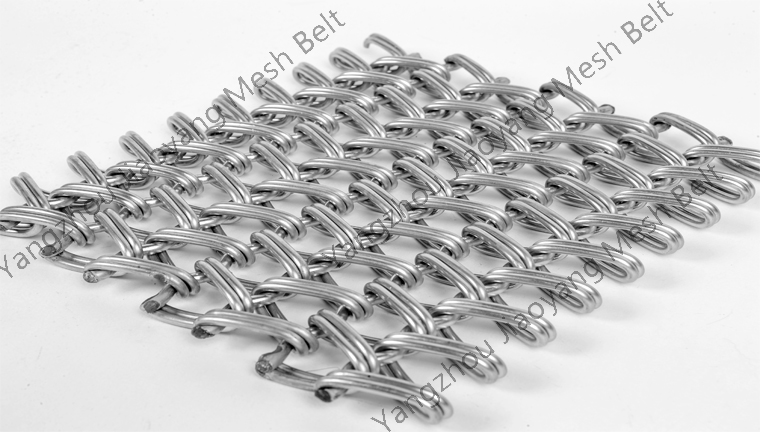
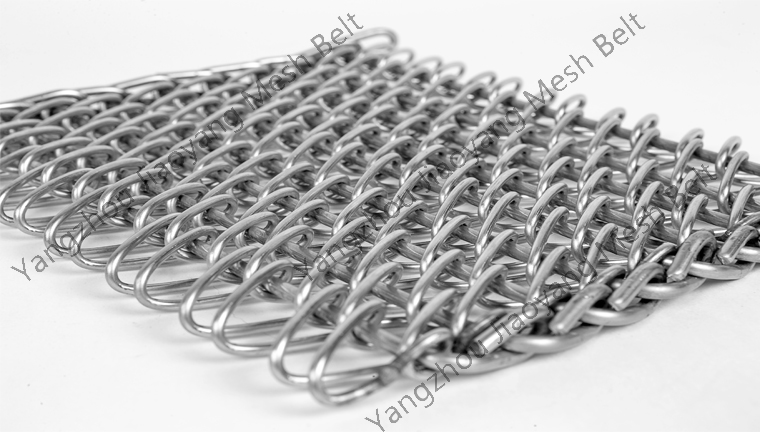
Surface quenching can improve the hardness and wear resistance of the steel surface, while overall quenching can make the steel reach a certain hardness as a whole.
1. Surface quenching
Surface quenching (Surface Hardening) is to heat the surface of the steel to a certain temperature and quench the surface of the steel to the required hardness to strengthen the hardness and wear resistance of the material surface. Common methods of surface quenching include flame quenching, plasma quenching and electron beam quenching. Among them, flame quenching refers to heating the workpiece with a flame, and then quickly immersing the steel surface in a coolant for quenching after heating to achieve the effect of increasing the surface hardness. Plasma quenching is to use the heat generated by plasma in the medium for heating and quenching, which has higher depth and strength than flame quenching; electron beam quenching refers to quenching after heating with an electron beam, which has higher power density and depth.
Surface quenching can improve the hardness and wear resistance of the steel surface, and is often used to manufacture high-precision mechanical accessories, tools and machine parts.
2. Overall quenching
Overall quenching refers to immersing the entire steel material in a quenching medium so that the steel as a whole reaches a certain hardness. The quenching medium for overall quenching includes water, oil, and polymers. Different quenching media will affect the quenching performance and hardness of the steel. Overall quenching can increase the overall hardness and strength of the steel and is widely used in vehicles, ships, machinery and other fields.
Since the quenching medium of overall quenching not only affects the steel as a whole, but also quenches the surface of the steel, the surface of the steel is hardened to a certain extent. However, the depth and degree of this surface hardening are far Less than surface quenching.
3. Surface hardness performance
The surface hardness performance of surface quenching and overall quenching is different. Surface quenching can form a high-hardness quenching layer on a relatively thin surface layer, which is harder and more wear-resistant than the hardened layer formed on the surface by overall quenching. Overall quenching is superior to surface quenching in terms of the hardness of the overall steel, and can increase the strength and hardness of the overall steel.
In addition, through the selection of reasonable quenching process and quenching medium, the properties of the hardened layer thickness and hardness of the steel can be adjusted and designed, so as to achieve customized quenching treatment for different workpieces.
【Conclusion】
Surface quenching and overall quenching are two commonly used quenching methods, which have a significant improvement effect on the hardness and wear of steel. Surface quenching mainly strengthens the hardness and wear resistance of the steel surface, while overall quenching can make the steel as a whole reach a certain hardness and strength. In specific applications, it is necessary to select the most suitable quenching method and quenching process according to the different needs of the workpiece.